outside screw and yoke
o s and y valve
one way check valve
ball check valve
Control valve CV refers to the flow coefficient of the valve. It applies to the factor of the head drop (Δh) or pressure drop (ΔP) over a valve with the flow rate Q.
Calculating Control Valve CV
When Sizing (calculating which size valve is needed for your application ) a control valve specialist needs to calculate the flow coefficient. A few key concepts that we need to clarify before we start with the math are pressure drop, flow rate, and their relationships.
Pressure drop: There will always be a pressure drop from the upstream flow to the downstream flow over a control valve, this is not caused by the valve alone but also by the system demand. To determine the pressure drop
you must subtract the outlet pressure (P2) from the inlet pressure (P1). This is a key element needed for the control valve sizing.
The relation between flow rate and pressure drop is an easy concept. The higher the flow rate through the valve ( restriction in process line) the greater the pressure drop.
The definition of Cv is the number of GPM (Gallons per minute ) that will pass through the control valve with a pressure drop of 1psi.
Control valve Cv refers to the flow coefficient of the valve. It applies to the factor of the head drop (Δh) or pressure drop (ΔP) over a valve with the flow rate Q. The formula will differ depending on the product the valve regulates, such as liquid, gas, or steam. The following article also gives a thorough explanation of the calculation of the flow coefficient:

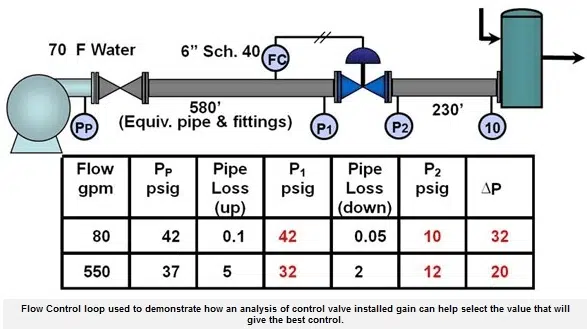
Also, the Cv varies across control valves because each valve lets the flow pass through differently. The difference in Cv relates to the type of valve and its opening position. When you need to do valve sizing for your application, you need the Cv to select the right valve.
Some vendors have standardized the flow coefficient (Kv). They created this standard using reference conditions, such as water at a specific temperature, flow rate, and drop pressure units. Keep in mind also that the Kv uses metric units and the Cv imperial units. Here’s the formula if you need it:
Kv = 0.865 · Cv
Kv is the flow coefficient in metric units. It is defined as the flow rate in cubic meters per hour [m3/h] of water at a temperature of 16 degrees Celsius with a pressure drop across the valve of 1 bar.
Cv = 1,156 · Kv
Cv is the flow coefficient in imperial units. It is defined as the flow rate in US Gallons per minute [gpm] of water at a temperature of 60℉ with a pressure drop across the valve of 1 psi.
Control Valves 101: Valve Types, Applications, Components, and Accessories
In Conclusion
Cv is just one of the technical terms for control valves, and if you are interested in more sizing processes for control valves, you can refer to our download page to see more calculations and sizing methods of control valves. All are free to download.
How to quickly understand various industrial valve types and their applications?